Poverty
The Governor’s 2024 Budget: Hits and Misses for Utah Families
Governor Cox unveiled his budget last week, and the general direction of the budget is positive. Voices for Utah Children is interested in some specific components of the budget that directly impact Utah children and their families:
Public Education
$854 million increase, including a 5% jump in per-pupil funding and $55 million for rural schools
This is a much-needed investment in public education. We support the focus on rural schools and are anxious to see the details as they emerge. Public education consistently polls as a top priority for Utahns of all political parties and backgrounds.
Support for Utah Families
$4.7 million to expand Utah’s child tax credit and $5 million for accessible child care
We appreciate the fact that the Governor has begun to address the urgent needs of Utah families with young children. However, both allocations fall far short of the amount required to truly support and elevate these young families’ current needs. A truly impactful child tax credit would require an investment of at least $130 million, and the benefits in reducing child poverty in Utah would be substantial. Our recent report on child care in Utah clearly illustrates the need for bold action to support families in the workforce, who are struggling with the cost and unavailability of child care. The Governor’s $5M project will help very few Utah families and does not address the true need.
Housing
$128 million for homeless shelters and $30 million for deeply affordable housing
We support the Governor in his effort to better support the homeless residents of our state. We encourage a greater focus on expanding support for homeless children specifically. Early care and education opportunities for young children as well as more supportive programs for their parents and caregivers are critical to helping families find stable housing and better future opportunities. Investing in deeply affordable housing will help many Utah families.
Behavioral/Mental Health
$8 million for behavioral and mental health
This is not enough to address the current mental health needs of Utahns – in particular, those of our children and the folks tasked with raising them. We need more mental health professionals and greater access to services. We know this is a major concern for the Governor and we encourage increased strategic investment in this area.
It is also important to acknowledge and applaud some items the Governor wisely left out of his proposed budget:
No Proposed Tax Cuts
Utahns want to see more invested in our children while they are young, to prevent greater challenges later in life. It is our children who suffer most, when politicians toss our tax dollars away on polices that mostly benefit the wealthiest 1% of Utah households.
No Proposed Funding for Vouchers
Public funds should not be redirected to private entities. Utah needs an annual audit of the current program, to assess who is benefitting from school vouchers. In other states, the results are not good – vouchers are looking more and more like a tax break for wealthy families.
Bold Investments Needed for Utah's Children
Governor Cox's budget focuses on increasing funding for education, families, and affordable housing.
These are all areas where we believe bold investment is needed. We support the Governor in addressing these issues, but cannot overlook how this budget falls short in the face of the ongoing struggles faced by Utah families with children.
We encourage our Legislature to use the Governor’s budget as a roadmap and increase the allocations to the amount needed.
Our 2024 Legislative Agenda
At Voices for Utah Children, we always start with this guiding question: "Is it good for all kids?" That remains our north star at the outset of the 2024 legislative session, and is reflected in our top legislative priorities.
So, what’s good for all kids in 2024?
A Healthy Start!
A healthy start in life ensures a child's immediate well-being while laying a foundation for future success. We are steadfast in our commitment to championing policies that prioritize every child's physical, mental, and emotional well-being. Central to this commitment is our focus on improving Utah’s popular Medicaid and CHIP programs, which are pivotal in the lives of many Utah children and families.
This legislative session, a healthy start for kids looks like:
- Empowering Expectant Mothers: We support a proposal from Rep. Ray Ward (R-Bountiful) to increase access to health coverage for low-income and immigrant mothers-to-be.
- Increasing Access to Health Care: We support bills that aim to improve access to the vital healthcare services children and parents need, especially for those on Medicaid and CHIP.
- Protecting Health Coverage: We oppose any effort to defund, and exclude deserving children from, the Medicaid and CHIP programs that help thousands of Utah kids every year.
Early Learning and Care Opportunities!
The formative years of a child's life lay the foundation for their future, shaping their cognitive abilities, socio-emotional skills, and passion for learning. We will support efforts to increase access to home visiting programs and paid family leave, but ensuring consistent, quality, and affordable child care is our top priority.
This legislative session, early learning and care opportunities for kids looks like:
- Bolstering Access to Quality Child Care: We support the efforts of both Rep. Andrew Stoddard (D-Sandy) and Rep. Ashlee Matthews (D-Kearns) to extend the successful Office of Child Care stabilization grant program that has supported licensed child care programs statewide.
- Investing in High-Quality Preschool: We support an anticipated legislative proposal to streamline Utah’s existing high-quality school-readiness program and to make it available to more preschoolers statewide.
- Recruiting and Retaining Child Care Professionals: We support Rep. Matthews’ proposal to expand access to the Child Care Assistance Program for anyone working in the child care sector.
- Building New Child Care Businesses: We also support Rep. Matthews’ proposal to continue funding for work to develop and support new child care programs in rural, urban, and suburban areas.
To view a more comprehensive list of our 2024 early care and learning legislative priorities, click here.
Economic Stability for Families with Children!
Economic stability forms the bedrock of thriving families and vibrant communities. To ensure that young families in Utah have the support they need to afford basic necessities, we will advocate for increasing families’ access to Utah's earned income and child tax credits.
This legislative session, economic stability for families looks like:
- A Little Extra Help in the Early Years: We support HB 153, Rep. Susan Pulsipher’s (R-South Jordan) bill to expand Utah’s new Child Tax Credit, (currently only for children ages 1 to 3), to apply to children between 1 and 5 years of age. We also strongly recommend helping even more Utah families with young children by making the tax credit available for families with any child between birth and 5, and expanding it to include the thousands of lower- and moderate-income families who are currently excluded.
- Credit for Working Families with Kids: We support HB 149, Rep. Marsha Judkins’ (R-Provo) bill to expand Utah’s Earned Income Tax Credit so that more lower- and middle-income families with children can benefit.
Justice for Youth!
We want to ensure that all youth, including those who come into contact with the juvenile justice system, have access to interventions and supports that work for them and for their families. We are dedicated to advancing policies and recommendations that contribute to a more fair and equitable juvenile justice system for all Utah youth.
This legislative session, justice for youth looks like:
- Prioritizing School Safety: We are monitoring bills from Rep. Wilcox (R-Ogden) and the School Safety Task Force, including: HB 14, “School Threat Penalty Amendments” and HB 84, “School Safety Amendments.” We remain hopeful that these efforts will support a secure learning environment for all students, without contributing further to the School-to-Prison Pipeline.
Be an Advocate!
As we chart the path forward, one thing remains abundantly clear: the well-being, growth, and future of Utah's children rely on the decisions we make today. Each legislative session presents an opportunity—a chance to reaffirm our commitment, reevaluate our priorities, and reimagine a brighter, more inclusive future for all.
Together we can continue to make Utah a place where every child's potential is realized, their dreams are nurtured, and their voices are heard.
Below are some ways you can get involved this session.
Stay Informed with our Bill Tracker
Stay informed about important legislation we are watching and reach out to your local representatives to let them know how you feel about legislation that is important to you. We make it easy for you to subscribe and watch bills that you are most concerned about.
Join us for Legislative Session Days on the Hill
Join us at the Capitol, where we offer attendees the opportunity to engage in the legislative process on a specific issue area (health and/or child care). You'll have the chance to attend bill hearings, lobby your legislators, connect with fellow community advocates, and watch House and Senate floor debates. Click the button below for the dates/times of our meetings and to RSVP.
Celebrate Utah's Immigrant Community
In collaboration with our partners at UT With All Immigrants, the Center for Economic Opportunity and Belonging, and I Stand with Immigrants, we are organizing Immigrant Day on the Hill. Join us to discover ways to engage in Utah's civic life. Enjoy food, explore resource tables, participate in interactive activities, and entertainment. Everyone is invited to attend this free event!
Event Details: February 13, 2024, 3:30pm-5:30pm at the Capitol Rotunda, 350 State St, Salt Lake City, UT 84103
Making Utah Taxes Fair for All Families
Most of us don't enjoy paying taxes. We do it, though, because pooling our money together through taxes makes it possible for us to have roads, schools, libraries and parks, fire fighters and law enforcement, and so many more public goods that none of us could afford on our own.
Tax policy (the ways we choose to collect taxes) impacts everyone, and often in many different ways. You may have very recently paid sales tax on your groceries, gas tax at the pump, property taxes on your home or through your rent, and of course, income tax on the money you earn.
From state to state, tax policy is unique; no two states collect taxes the same way. Tax policy also changes a lot over time. Different types of taxes affect people differently, depending on whether they have higher or lower incomes.
Some tax policies and structures promote fairness and equity. Other approaches to taxes contribute to social inequality. When tax policies burden lower-income people more than very wealthy people, who can more easily afford to pay higher taxes, we consider that unfair. Sometimes those kinds of tax policies are called "regressive."
States with the most unfair tax structures typically have:
- have no or little income tax,
- have no refundable tax credits, and
- rely on high sales and excise* taxes.
How Fair is Utah's Tax Structure?
Analysis by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) shows that in Utah, low- and middle-income families pay more of their income in taxes than the wealthiest households.
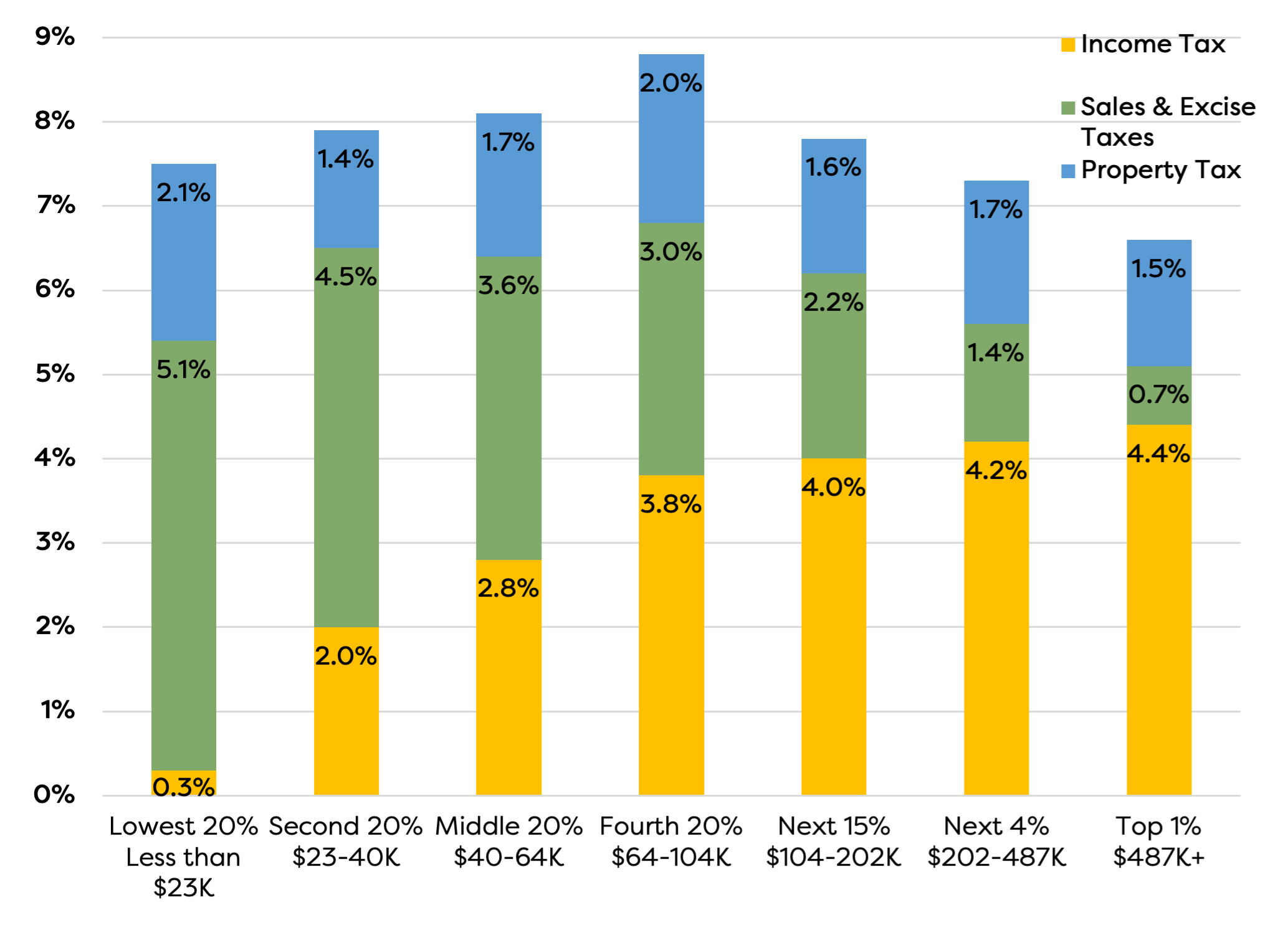
We judge Utah's tax fairness holistically, by looking at all the taxes that are paid by families at different income levels. This is the "effective tax rate," or the share of overall household income a family spends on income, sales/excise and property taxes in a year. The table below shows the effective tax rate of Utah households, depending on how much income they earn each year.
In Utah, 20% of families make less than $23,000 per year. These families pay approximately 7.5% of their total income in state and local taxes. By comparison, the top 1% of Utah families - which are earning more than $487,000 per year - pay an effective tax rate of only 6.6%.
But the Utah families who pay the most in taxes are those in the middle. Middle-income households (making between $40,000 and $104,000 per year) have an effective income tax rate from 8.1% to 8.8% - the highest effective tax rate of all income levels.
 Towards Fairness: Tax Credits that Actually Work for Working Families
Towards Fairness: Tax Credits that Actually Work for Working Families
One way to make our state tax structure more fair is through carefully constructed income tax credits. When tax credits cut out families that pay less in income tax - like our non-refundable Earned Income and Child Tax Credits - then the families who are struggling most, benefit the least. Some legislators argue that families who don't pay as much income tax don't "deserve" to fully benefit from tax credits. But those families clearly pay more in overall taxes than any other income group.
Babies don't pay any taxes - but the households they live in do. Working families with young children deserve a tax system that supports them as they care for and raise the future leaders of our state. Having a fair tax structure in Utah means making sure children, and the households they are living in, have enough money to afford the things they need.
Learn How Better Income Tax Credits Help Families
Glossary
Effective Tax Rate: the share of income a family spends on taxes. This is calculated by dividing the amount families pay in taxes by their annual household income.
* Excise Tax: a tax directly levied on certain goods by a state, such as fuel, liquor, or cell phone plans. They are paid by the merchant before the goods can be sold and passed to the consumer through higher prices before the sales tax is added.
Nonrefundable Tax Credit: reduces the taxes owed - allows a taxpayer to only receive a reduction of their tax liability until it reaches zero.
Refundable Tax Credit: allows a taxpayer to receive a refund if the credit they receive is greater than their tax liability.
Tax Credit: a dollar-for-dollar amount that a taxpayer claims on their tax return to reduce the income tax they owe. You can use this to reduce your tax bill and potentially increase your refund amount.
Tax Liability: the amount of taxes owed by a taxpayer to the government before taking into account allowable tax credits.
Tax Policy: policies that determine how we to collect taxes.
Take Action on EITC Awareness Day
January 26th is Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) Awareness Day! The EITC is a vital tool in reducing child poverty, and improving the long-term outcomes for children across our state.
Some tax policies - like the EITC - promote fairness and equity. Others make social inequality worse - we call those policies “regressive;” Regressive policies disproportionately hurt lower-income individuals while disproportionately benefiting rich people. That simply isn’t fair.
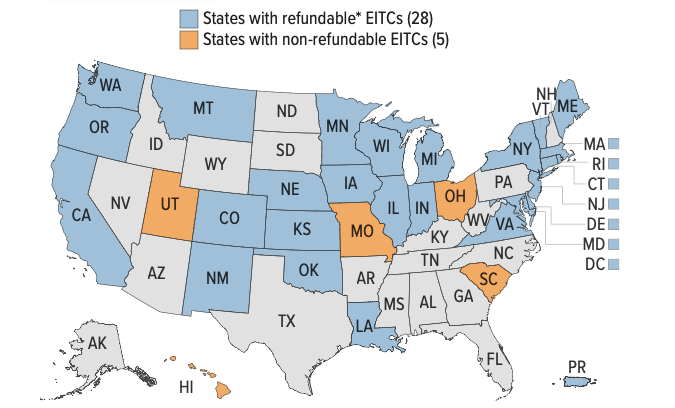
Utah was ranked 29 out of 50 states (plus the District of Columbia) in a recently released report from the Institute of Taxation and Economic Policy (ITEP) —-ITEP uses a “tax inequality index” to measure the effects of each state’s tax system on income inequality. Data from ITEP shows that lower and middle-income households pay a larger portion of their income in taxes overall, when compared to wealthier households. Middle-class families pay the highest effective tax rate (income tax, sales tax, other taxes and fees), while the wealthiest 1% of Utah households pay the least of all (see table below).
Thirty-one states and the District of Columbia have a state Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC). Utah is one of only five states that excludes the poorest working families from benefiting from their state EITC, by making their EITC non-refundable. By contrast, many states have taken steps to ensure that their state EITC includes as many low- and middle-income families as possible. In 2024, Utah legislators will have a chance to help more Utah families, too - by making our state EITC refundable.
Support HB 149: Make Utah's EITC Refundable!
This year, Representative Marsha Judkins (R-Provo) is championing HB149, which would transform Utah’s EITC into a refundable credit. This bold change will help many more families to afford essential necessities for their children's well-being, such as food, clothing and medical care.
On this EITC Awareness Day, let's make some noise! Reach out to your state legislators, remind them why this policy is impactful for families and children, and help us advocate for a more fair and equitable tax system.
To learn more about the Earned Income Tax Credit, see here.
Empower Utah Families with Better Income Tax Credits
When it comes to improving the lives of hardworking Utahns, we need policies that help those who are struggling to make ends meet. A refundable Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) could do just that.
Let's start by discussing what the earned income tax credit is and how it benefits working families and children.
What is an Earned Income Tax Credit?
You may already know about the federal Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC). It is a refundable federal income tax credit for low- and moderate-income working people, that was created to support people who are in the workforce but need extra support to meet their families' needs. To claim the federal EITC, you must have earned income and everyone on your tax return must have a social security number.
The amount of your credit will be determined by your family's earnings, as well as the number of children you have. The EITC credit may help to reduce the amount you owe on your federal taxes - and if the EITC amount is higher than the federal taxes you own, you can actually get money back from the government.
The EITC is a critical policy tool to support financial stability in working families. Even just a few hundred dollars a year can help families stay current on bills, purchase groceries, afford car repairs, or pay down debt.
How does Utah's Earned Income Tax Credit work?
Because the federal EITC has been so effective at supporting working families, many states have created their own Earned Income Tax Credits in order to help these families even more. Currently 31 states offer a state EITC. Utah enacted a limited EITC for families with children in 2022.
Calculating your state Earned Income Tax Credit amount in Utah is easy: it will be 20% of whatever your federal EITC amount is when you file both your federal and state taxes. However, due to the way it was structured by the state legislature, Utah's EITC currently excludes many hardworking families who should benefit. 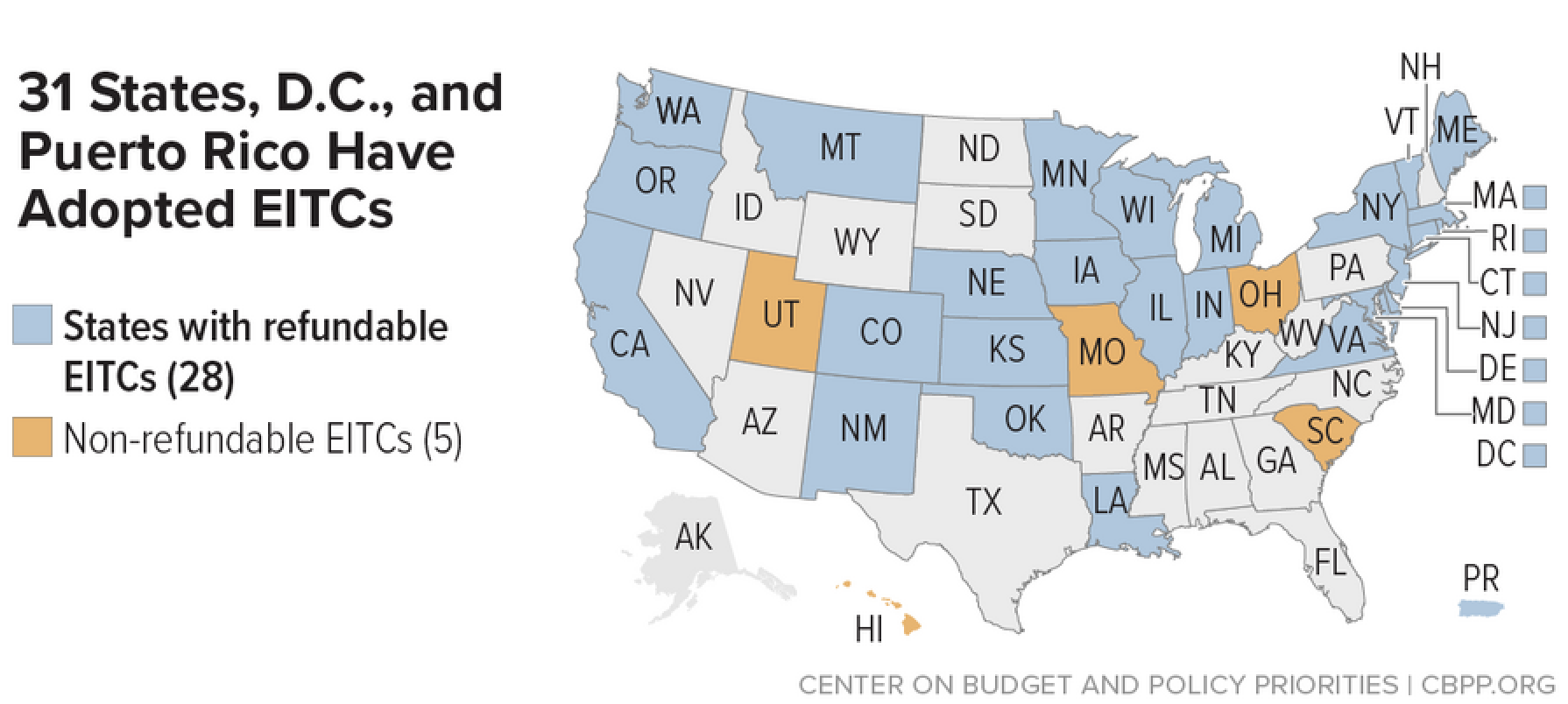
Our state EITC's biggest limitation is that it is "non-refundable." Utah is one of only five states with this exclusionary policy. Unlike the federal EITC, Utah's tax credit can only be applied to the income taxes you owe. You will never receive any money back from claiming the state EITC. Unless your state taxes add up to the amount of the state EITC you are allowed to claim, or more than that amount, your family misses out on the full benefit.
A refundable state EITC is a simple and cost-effective way to level the playing field for Utah families. These days, families who don't make a lot of money struggle to afford to live and raise a family in Utah. Especially for families with young children, who are just starting out in their careers, every little bit of extra financial support really helps.
State leaders say that our state EITC is meant to provide a maximum benefit for working families with children, with annual (adjusted) incomes between $11,000 and $26,000. Imagine a family with two young children, where one parent is still in college, and the other parent works only 32 hours a week. Because Utah's EITC is not refundable, none of the struggling families in this income range will see any benefit from the tax credit.
Though they don't make a lot of money, these people actually pay more taxes, as a percent of their income, than the wealthiest people in Utah. These hard-working families deserve a refundable state tax credit.
Our state EITC policy also requires that your earned income must be reported on a W-2 form, as proof of your work. This requirement means the state EITC can't be claimed by self-employed people, people who work on contract and people who participate in the "gig economy" (such as driving for Lyft or watching pets through Rover). Even though these workers may be eligible for the federal EITC, they can't benefit from the state credit because they don't receive a W-2 to recognize their hard work.
What is Refundability?
A refundable tax credit means that if the amount of the credit is more than the amount of taxes you own, you can get the extra amount back as a refund payment!
A non-refundable tax credit means that the amount of the credit can only ever offset the amount of taxes you owe. You can't benefit from any portion in excess of the income tax you owe, and you can't carry any unused portion of the credit over into another tax year.
Here's how this difference plays out in Utah for a married couple with two children, filing their taxes jointly. In this hypothetical family, one parent earns $39,000 working full-time (about $19/hr), and they only owe $200 in state income tax. If Utah’s EITC were refundable, they would realize the full benefit of the credit by receiving a refund of $300. Because our state EITC is non-refundable, that $300 just disappears. After it cancels out the $200 in taxes the family owes, Utah's EITC stops working.
In the coming year, legislators have the opportunity to empower working families in Utah with a much better Earned Income Tax Credit. By making our state Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) refundable, state leaders could tangibly enhance the lives of these families, providing them with essential financial support needed for their daily well-being. If you're curious about the significance of equitable tax policies and the intricate web of tax distribution, learn more by following the link provided below.
Glossary
Tax Credit: a dollar-for-dollar amount that a taxpayer (s) claim on their tax return to reduce the income tax they owe. You can use this to reduce your tax bill and potentially increase your refund amount.
Tax Liability: the amount of taxes owed by a taxpayer to the government before taking into account allowable tax credits.
Nonrefundable Tax Credit: reduces the taxes you owe --- allows a taxpayer to only receive a reduction of their tax liability until it reaches zero.
Refundable Tax Credit: allows a taxpayer to receive a refund if the credit they receive is greater than their tax liability.
Sources
- https://www.cbpp.org/research/federal-tax/the-earned-income-tax-credit
- https://www.cbpp.org/blog/many-states-are-creating-or-expanding-tax-credits-to-help-families-afford-the-basics
- https://www.cbpp.org/research/state-budget-and-tax/states-can-enact-or-expand-child-tax-credits-and-earned-income-tax
- https://www.irs.gov/credits-deductions/individuals/earned-income-tax-credit-eitc
- https://www.irs.gov/newsroom/tax-credits-for-individuals-what-they-mean-and-how-they-can-help-refunds#
- https://itep.org/whopays/utah/
- https://taxfoundation.org/taxedu/glossary/tax-refund/
Tax Policy 101: What is Refundability?
Tax policy is complicated. Talking about taxes involves jargon, and concepts that can be confusing. For example, what is a 'refundable' tax credit? What exactly does that mean, and how does it help families? We answer these questions here with a quick breakdown of what refundability is and how it impacts families.
What is a "refundable" tax credit?
When a tax credit is refundable, it is available to all families. Even if a family doesn’t owe anything when they file their income taxes, a refundable tax credit makes it possible for them to get money back in the form of a tax refund. Families can then use that money to pay for necessities.
What is a "non-refundable" tax credit?
A non-refundable tax credit can only ever be used to pay for taxes. If a family doesn’t owe any taxes after deductions, they can’t access any of the tax credit. If the family only owes a little in income taxes, they can only use the non-refundable credit to pay down whatever they owe.
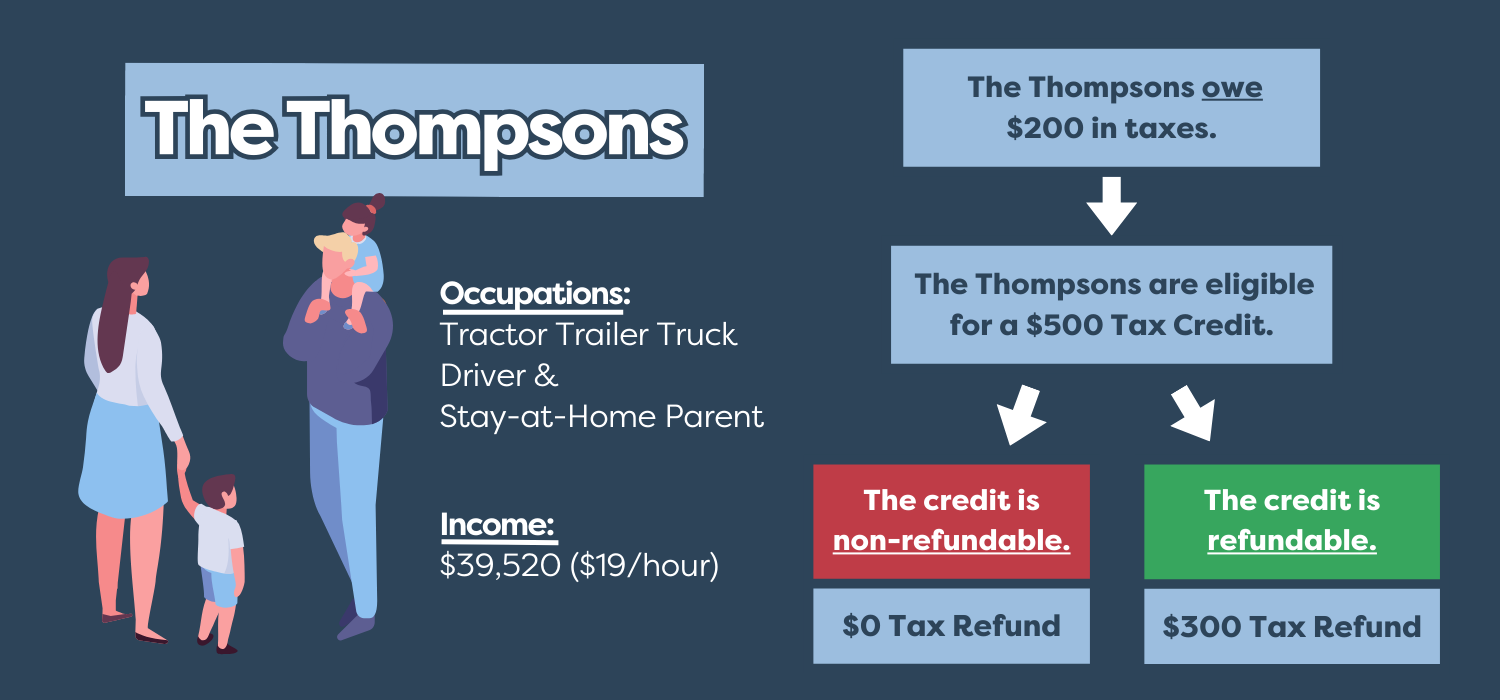
How does refundability impact a family like yours?
In the illustrated example below, the Thompsons have two young children and make a family household income of $39,520 for the year. Based on their income and after deductions, they owe $200 in taxes. Now imagine they qualify for a $500 tax credit. Refundability can greatly impact how much they owe in taxes and whether they'll keep more of their earnings through a refund.
If the $500 tax credit is non-refundable, it will be applied to offset what the Thompsons owe in taxes. Since they owe $200, the credit will help reduce the amount they owe to $0 – a positive outcome.
However, an even better outcome for young families arises when that $500 tax credit is refundable. If refundable, the $500 tax credit can go towards the amount they owe in taxes ($200) and the remaining amount of $300 would go back to the Thompsons as a refund. This $300 can help with expenses like car repairs, new winter coats for the kids, and baby formula. Though it may not seem like a lot, families facing financial challenges can make good use of this help.
To learn more about making Utah’s EITC refundable, go here.
To learn more about making Utah’s CTC refundable, go here.
To read about other refundable tax credits in Utah, go here.
Glossary
Tax Credit: a dollar-for-dollar amount that a taxpayer (s) claim on their tax return to reduce the income tax they owe. You can use this to reduce your tax bill and potentially increase your refund amount.
Nonrefundable Tax Credit: reduces the taxes you owe --- allows a taxpayer to only receive a reduction of their tax liability until it reaches zero.
Refundable Tax Credit: allows a taxpayer to receive a refund if the credit they receive is greater than their tax liability.
Tax Policy: policies that determine how we collect taxes.
Tax Cuts Hurt Kids
Why Voices Opposes Proposed Income Tax Cuts
Over the past four years, Utah's Legislative Leadership has consistently prioritized tax cuts above the needs of Utah's families. Despite a $400 million tax cut passed last year that benefited the most wealthy Utahns, and now fearmongering about a supposed $130 million budget shortfall, Legislative Leadership is yet again pushing for another $170 million in tax cuts.
As the 2024 Legislative Session unfolds, many legislators will claim a need to curb spending and tighten purse strings - that we can’t afford to fully fund social services or any new programs. The question arises: How can we afford $160 million in tax cuts when many crucial needs remain unmet? In a time when working families are struggling to afford groceries, granting more tax cuts to the wealthy is a step in the wrong direction.
Who Benefits from the Proposed Tax Cuts?
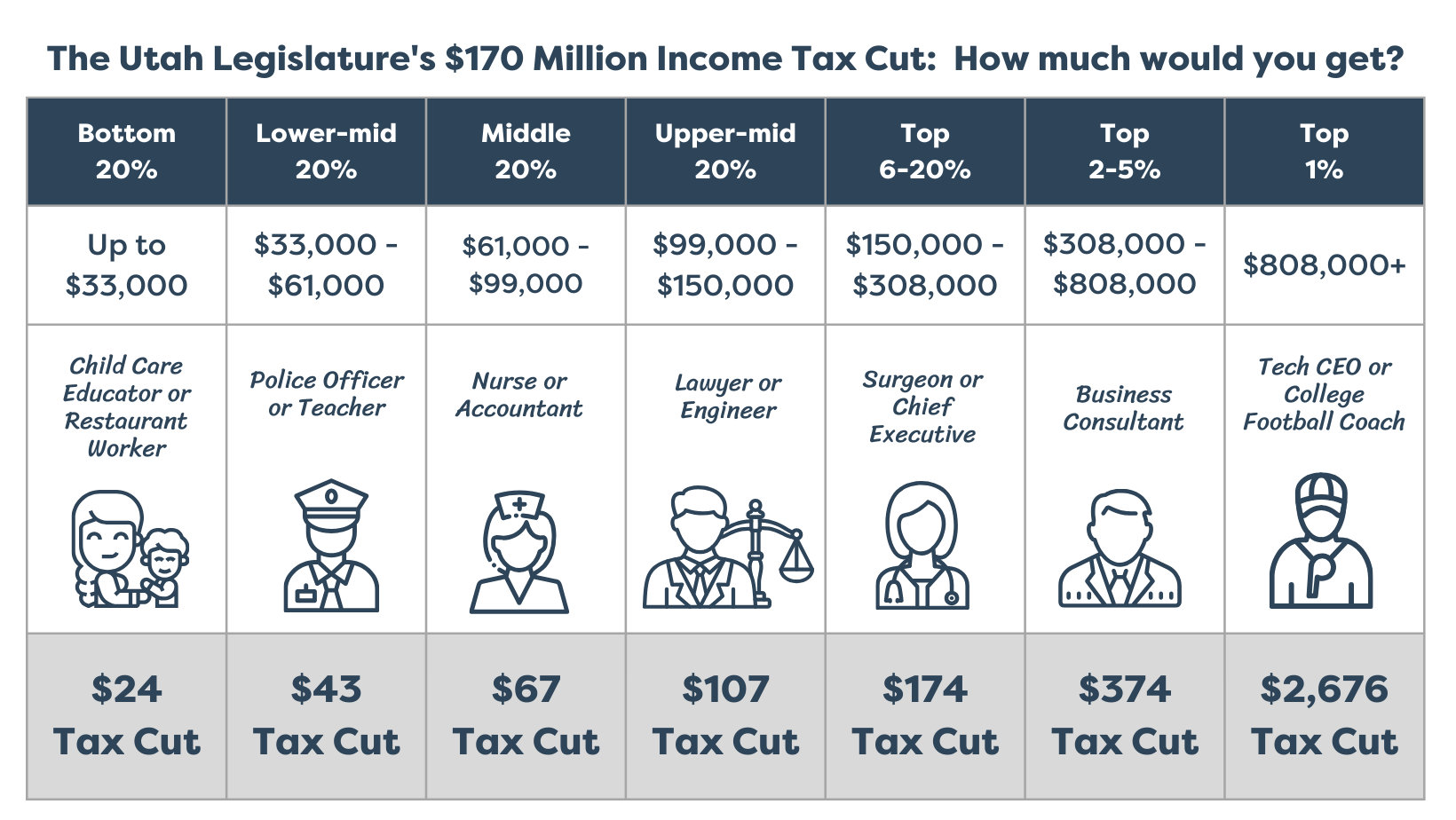
The proposed tax cut will help the richest 1% more than anyone. Our analysis shows the proposal will save the bottom 80% of Utah earners between $24 and $107. While the top 1% of Utah earners will save a whopping $2,676. These tax cuts will not provide real help to working families.
Out of the proposed $170 million tax cut, $40 million will go to the top 1% of Utah's wealthiest individuals. In contrast, the bottom 80% will split about $61 million.
Note: This image was updated to reflect the changed fiscal note for SB69, increasing the estimate from $160 Million to $170 Million on 2/23/24.
Utah's Unfair Tax Code
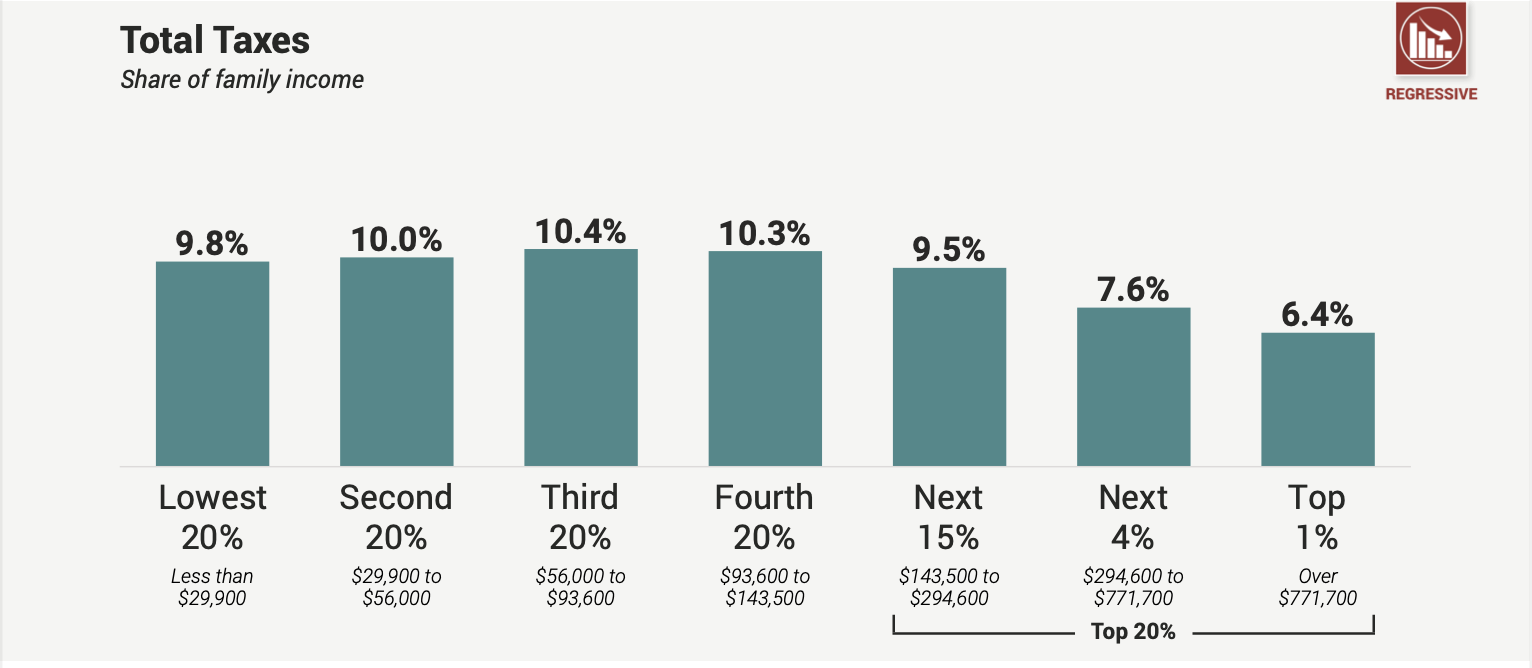
Contrary to the argument that the top 1% pays more in taxes, the reality is that low- and middle-income families bear a higher tax burden. Families making less than $29,900 per year pay 9.8% of their total income in state and local taxes, while the top 1% pays an effective tax rate of only 6.4%.
Why Voices Opposes the Proposed Income Tax Cuts
Voices for Utah Children opposes the proposed tax cuts due to the unmet needs of children and families in Utah. Our income tax should be used to increase funding for education, child care, nutrition, mental health programs, and other services with long-term societal benefits.
The appeal of tax cuts fades when we realize it means losing essential services. Children need us to be their voice, and we need to show up and advocate for their future. It's not just the right thing to do for them; it's a move that benefits all of Utah. Here's why investing in children pays off:
- Investment in the future: Children are the future, and investing in their well-being leads to positive long-term outcomes. Early childhood interventions improve educational attainment, job prospects, and overall health, benefiting society as a whole. This includes supporting our child care system, which is facing a loss of nearly $600 million in federal support this year.
- Promoting equality: Programs for children often target low-income families and disadvantaged communities, narrowing the gap in opportunities and promoting a fairer society. Access to quality education, healthcare, and essential services can break the cycle of poverty, creating an even playing field for every child.
- Stimulating the economy: A healthy, educated population contributes to a stronger economy. Investments in children's programs create a ripple effect, boosting productivity, encouraging innovation, and fostering economic growth in the long run.
We need to hit pause on tax cuts and instead acknowledge that investing in children is the better path to follow. It will lead to a stronger and more prosperous Utah, and those benefits will far outweigh any tax cut currently being considered.
Utah Children's Budget 2023
The care for the children in our state and communities can be measured by our public investment in our smallest humans. From the fiscal year 2008 to 2022, Voices for Utah Children divided all state programs concerning children into seven categories, without regard to their location within the structure of state government to quantify the level of public funding and identify trends. The seven categories are:
- K-12 Education
- Health
- Food & Nutrition
- Early Childhood Education
- Child Welfare
- Juvenile Justice
- Income Support
An appendix of our tables, sources, methodology and description of programs can be found here.
How Much We Spend
The interactive circle chart below compares how much we spend by category, program, and source of funding, just use the filter and click the category to zoom in.
-
K-12 Education makes up 92% of the state-funded portion of the Children’s Budget, while the federal-funded portion is more diversified across categories.
Spending Trends
We compare the budget to FY2008 because that was a peak year in the economic cycle before The Great Recession and all figures have been adjusted for inflation, so they are comparable across time.
- From FY2008 to FY2022, total public investment in children increased by 43%, growing much faster than Utah’s public-school enrollment (district & charter schools) by 26%, or the child population ages 0-17 by 13% from 2008-2021.
The federal share of the Children's Budget has fluctuated between 18-26% but had its biggest increase at the beginning of the Great Recession and the Covid-19 Pandemic. This is also when state funding for the Children's Budget has declined, for example real state & local K-12 education funding fell by $206 million since FY2020, the largest two-year decline since the Great Recession in 2008-2010. Several years after the Great Recession the federal share of the Children’s Budget decreased and the state share started to increase again, something that will hopefully happen again as pandemic relief funding rolls back.
Funding Sources: Federal vs. State
When the categories are disaggregated by source of funding, Food & Nutrition, Income Support, Health, and Early Childhood Education programs are mainly funded by federal sources, and Child Welfare, K-12 Education, and Juvenile Justice programs are funded mainly by state sources. And since Amendment G passed and allowed the income tax to be used to fund programs for children (in addition to K-12 and some Early Childhood Education & Nutrition Programs), the Child Welfare, Juvenile Justice, and Health categories are funded primarily by the income tax. In FY2022, 98% of Juvenile Justice, 100% of Child Welfare, and 88% of Health categories of the state funded Children's Budget were funded by the income tax totaling to $475 M.
When examining the state-funded portion of the budget since FY2008 each category has a different story.
- Juvenile Justice programs declined the most in dollar amount, $32.9 M or 28% mainly due to a reduction in correctional facility and rural programs and it also had an increase in early intervention services which advocates consider to be a goal of juvenile justice reform.
- Child Welfare programs declined by 16% or $21.8 M, mainly from the Service Delivery program which funds caseworkers to deliver child welfare, youth, and domestic violence services.
- Income Support declined 49% or $2.1 M and appears to be more cyclical, rising and falling with the Great Recession. Interestingly, the TANF grant is a mix of state and federal funds, and only a small amount goes to Income Support or cash assistance.[i]
- Food & Nutrition increased by 56% or $19.7 M due to an increase in liquor & wine tax revenues which supports the school lunch program.
- Early Childhood Education had the largest percentage increase of 109% or $42.0 M mainly from the Upstart program but increasing in every program except Child Care Assistance.
- Health has increased by 80% or $139.3 M from the Medicaid and CHIP program but also had a 58% or $12.4 M decrease in Maternal & Child Health.
- The category that has increased the most in dollar amount is K-12 Education.
K-12 Education Funding
State and local sourced funding for K-12 education increased by $1.6 billion in constant 2022 dollars from FY2008 to FY2022, but per-pupil spending only increased from $10,212 to $10,537 per student. This means that even though more is being spent in total dollars, it barely covers the increase in students during the same time.
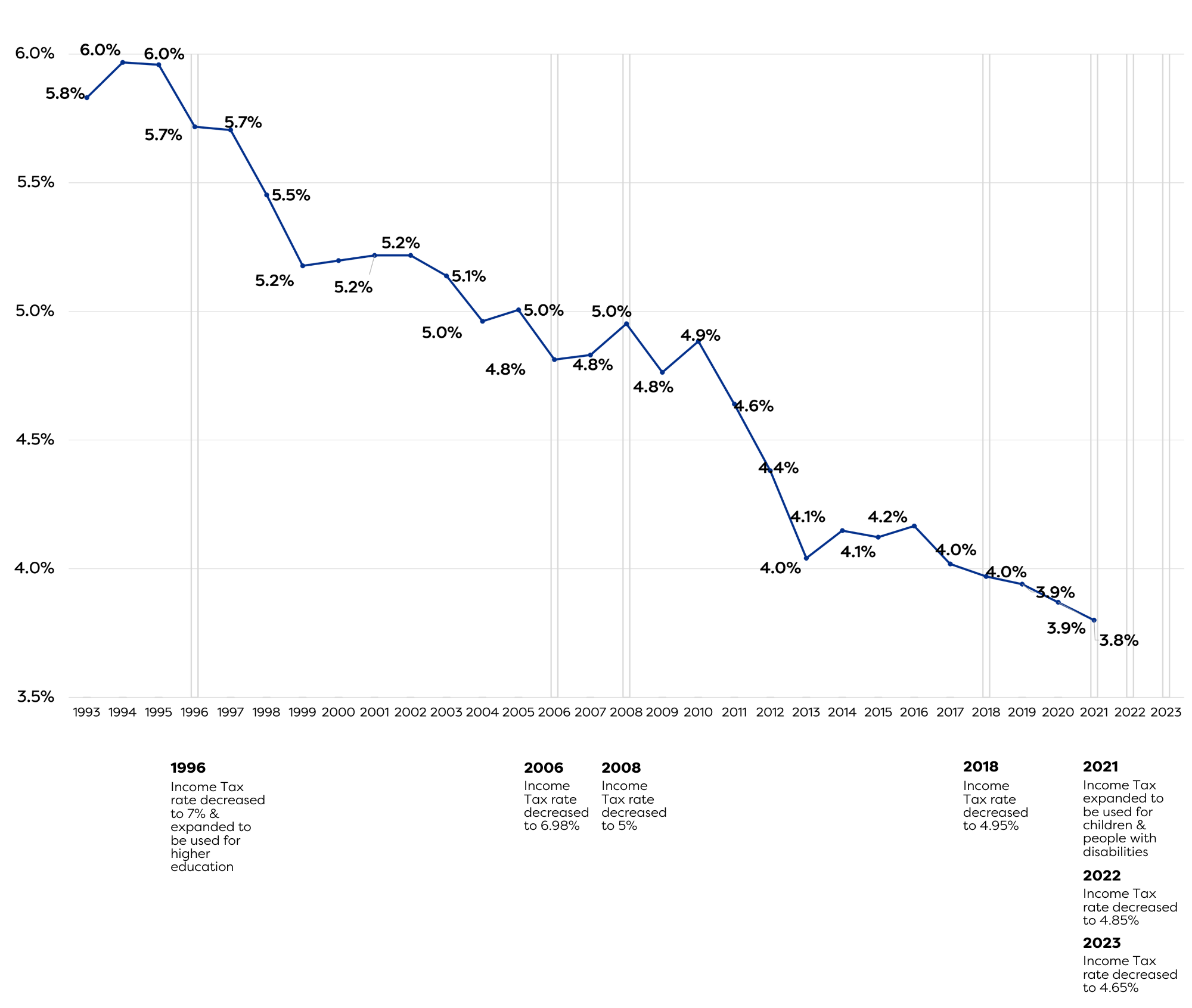
In 1948, 100% of the income tax was allocated to public education, an increase from 75% when it was originally imposed in 1931. It was expanded in 1996 to include higher education, in 2021 to include non-education services for children and people with a disability, and may be expanded again depending on a 2024 ballot measure placed by the Utah Legislature.
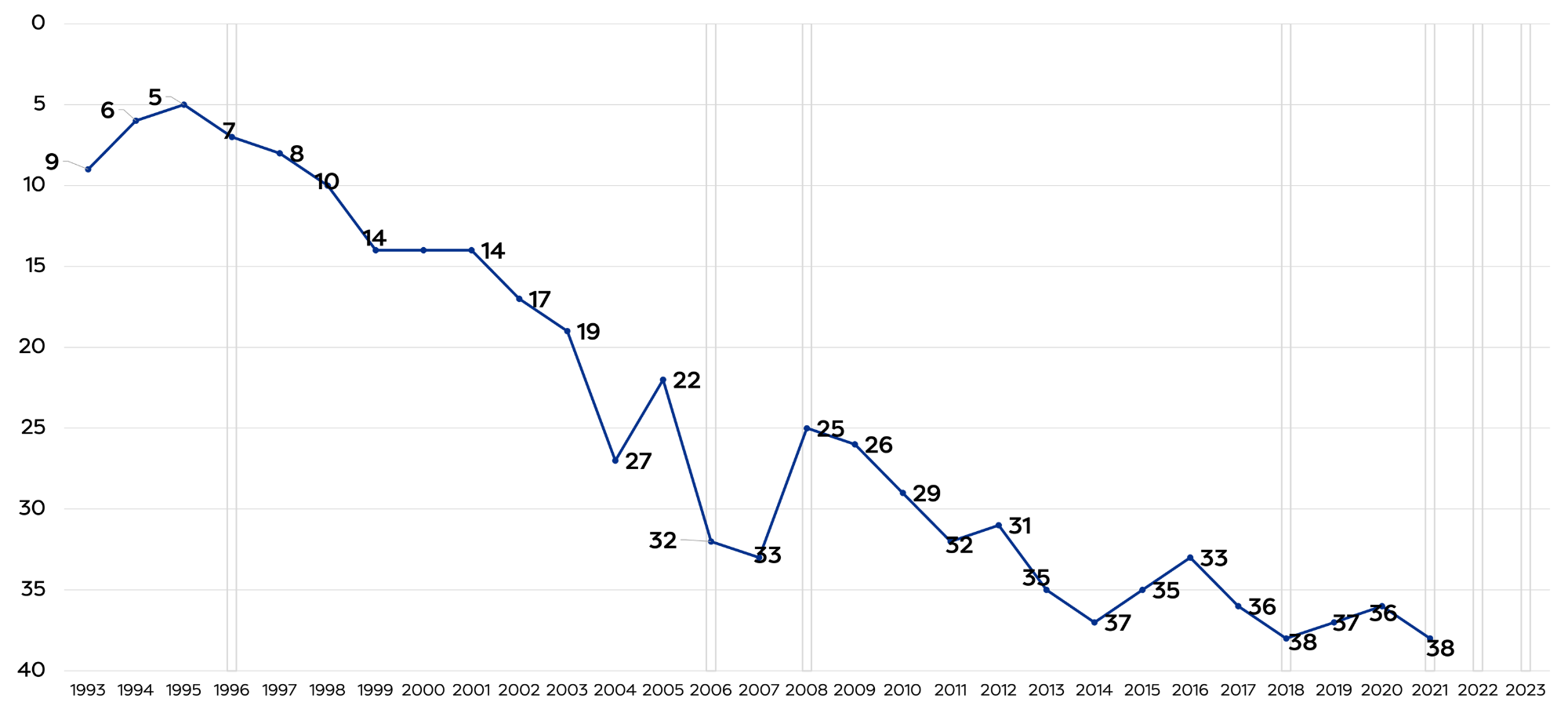
The income tax rate has been reduced in 1996, 2006, 2008, 2018, 2022, and 2023. The graphs below illustrate a timeline of these changes and Utah’s total elementary and secondary public schools (district & charter) funding effort (including capital) as a percentage of personal income and rank compared to other states.
Unfortunately, the result is a downward trajectory and likely explains our second to last place in per-pupil funding in the country.[ii]
Utah's Education Funding Effort as a Percent of Personal Income
According to the fiscal notes, the last two bills that reduced the Income Tax rate in 2022 and 2023 estimated a loss of $1.3 billion in the Income Tax Fund from FY2022-2025 with more ongoing.[iii]
State & Local Funded Portion of K-12 Education
Another result of these changes has been shifts in the funding source for K-12 education. From the fiscal year 2008 to 2022, the federal-funded portion increased by 74% and the state-funded portion declined by 3%.
Meanwhile, Local sources have increased by 12%, possibly to meet the needs of their communities while state-funded sources decline and putting greater pressure on sources like the property tax which is more regressive than the income tax because it takes a greater toll on low-and middle-income families.
Rank of Utah's Education Funding Effort Compared to Other States
We Need to Prioritize Children in the Budget
While Utah doesn’t have the most kids than any other state, we do have the highest share of kids in our population. And we as a community are entrusted to make sure they are cared for, safe, and have the tools they need to achieve their aspirations. As the Utah Legislature drafts, holds hearings on, debates, and passes the Utah state budget we hope they prioritize our most vulnerable and precious group, Utah’s children.
[i] https://www.cbpp.org/sites/default/files/atoms/files/tanf_spending_ut.pdf
[ii] https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/school-finances.html
[iii] https://le.utah.gov/~2022/bills/static/SB0059.html, https://le.utah.gov/~2023/bills/static/HB0054.html These fiscal notes show the loss from the income tax fund but they are not disaggregated by changes from the income tax rate or tax credit portion of the bills.
Invest in Utah's Future Coalition: $5.6b of unmet needs should be prioritized over tax cuts
BROAD COALITION CALLS FOR INVESTMENT IN UTAH’S FUTURE RATHER THAN TAX CUTS, DOCUMENTS $5.6 BILLION IN URGENT UNMET NEEDS
Salt Lake City – On Monday, January 23, 2023 at the Utah State Capitol, a broad and diverse coalition of advocates for the poor, for disabled Utahns, for education, health care, clean air, the Great Salt Lake, transportation investment, and a variety of other popular Utah priorities held a press conference calling on the Utah Legislature to prioritize addressing Utah’s long and growing list of unmet needs over permanent tax cuts that undermine our long-term capacity to invest in Utah’s future.
Utah’s strong economy and rapid recovery from the pandemic, combined with the ongoing impact of federal spending, have generated unexpected state revenues amounting to a reported $3.3 billion available for FY2024. These revenues put Utah in a position to address chronic revenue shortages that have plagued numerous areas of state responsibility. Instead, state leaders have proposed roughly half a billion dollars in permanent tax cuts, tilted unfairly toward the high end of the income scale, as well as additional hundreds of billions in one-time tax breaks.
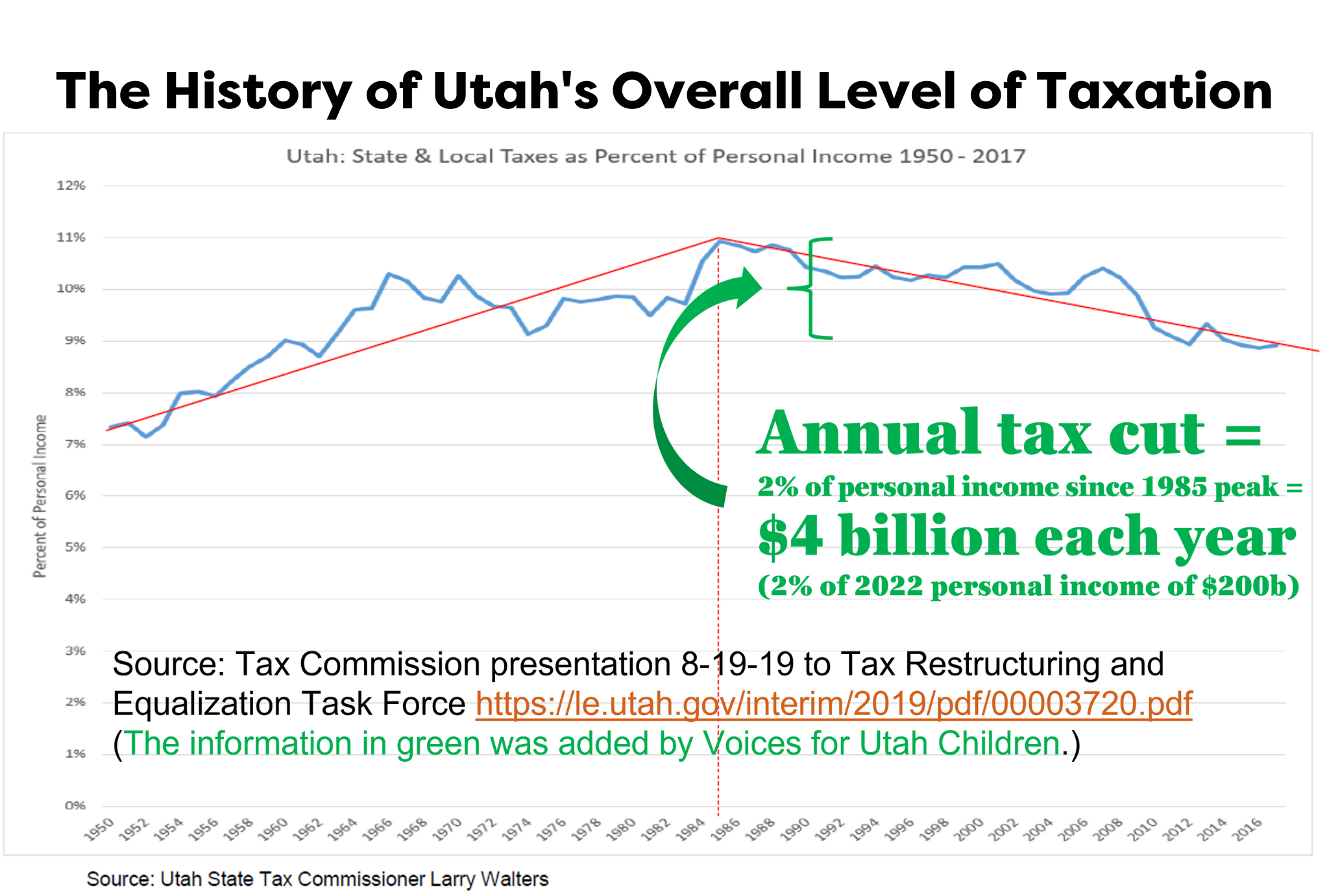
These new proposed permanent tax cuts would be over and above the roughly $4 billion that the Legislature has already cut from annual revenues in recent decades, leaving Utah’s taxes at their lowest level in half a century, relative to incomes.
In response, today the Invest in Utah’s Future coalition presented a list of urgent unmet needs amounting to $5.6 billion, over $2 billion more than the amount of the “surplus” revenues.
The advocates also pointed out that, according to data from the Utah State Tax Commission and the Utah Foundation, taxes in Utah are the lowest that they have been in decades, following repeated rounds of tax cutting. “Of course we all like paying lower taxes, but at a certain point we have to ask ourselves: Is it possible to have too much of a good thing? Are we, as the current generation of Utahns, meeting our responsibility, as earlier generations did, to set aside sufficient resources every year to invest in our children, in our future, in the foundations of the next generation’s prosperity and quality of life?” said Matthew Weinstein of Voices for Utah Children.
Speakers also referenced public opinion surveys by the Deseret News and Hinckley Institute that found that only 25% of Utahns support tax cutting over investing in Utah’s future, consistent with other polls done in recent years by the same organizations as well as by Envision Utah and the Utah Foundation.
Here is the list of urgent unmet needs that Utah has not been able to address due to the state’s chronic revenue shortages:
| Budget Area | Amount | Details | Contacts |
| K-12: Reduce class sizes from 29 to 15 | $1.1 billion ($612m K-6 only) |
Reduce class sizes/improve student/teacher ratio below the current Utah average of 29 (vs national average of 24) to optimum class size of 15. |
Utah Education Association Director of Policy and Research Jay Blain |
| K-12: Paraeducators | $312 million |
Expand paraeducators to all Utah elementary classrooms. |
Utah Education Association Director of Policy and Research Jay Blain |
| K-12: Increase school counselors | $130 million | Increase school counselors per student to the national standard optimum of 1:250. Utah’s current ratio is 1:648, compared to the national average of 1:455. | Utah Education Association Director of Policy and Research Jay Blain |
| K-12: school psychologists, social workers and special ed teachers | $285 million | Increase student access to school psychologists, social workers and special ed teachers.
Current and optimal ratios are: School psychologists: Now 1:1950/Optimal 1:500 Social workers: Now 1:3000/Optimal 1:250 Special ed teachers: Now 1:35/Optimal 1:25 |
Utah Education Association Director of Policy and Research Jay Blain |
| K-12 Education: reduce teacher attrition and shortages | $500-600 million | Envision Utah estimates that we need to invest an additional $500-600 million each year just to reduce teacher turnover, where we rank among the worst in the nation. Our leaders’ unwillingness to solve our education underinvestment problem is why the majority-minority gaps in Utah’s high school graduation rates are worse than nationally and our younger generation of adults (age 25-34) have fallen behind their counterparts nationally for educational attainment at the college level (BA/BS+). | |
| K-12 School Nurses | $78.5 million | The Utah Dept of Health annual report “Nursing Services in Utah Public Schools 2021-22” found that it would cost $78.5m to hire an additional 785 nurses so as to have one nurse in every public school building. There are currently only 261 nurse FTEs in Utah’s public schools, a ratio of 1 nurse for every 2,583 students. One nurse in every building would improve that ratio to 1:644, which would still be worse than the national average. https://heal.health.utah.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/2022-Nursing-services-in-Utah-Public-schools-8-22-22-ADA.pdf |
Dr. William Cosgrove, Past-President, American Academy of Pediatrics – Utah |
| Full Day Kindergarten | $70 million | Gov. Cox is proposing $70 million in the FY24 budget to make full-day Kindergarten available to all Utah families who would choose to opt in to it. | Voices for Utah Children Anna Thomas |
| Child Care | $236 million |
$236 million is needed to continue stabilizing the child care industry as federal funds are depleted. This funding will allow for the continuation of child care stabilization grants, retention incentives for early childhood professionals, the coverage of licensing-related fees in order to lessen the barriers to expanding, maintaining, and opening new child care programs, and regional child care outreach grants for rural and urban child care deserts. Source: www.utahcareforkids.org/get-involved/2023-legislation |
|
| Pre-K and Child Care | $1 billion | Well over $1 billion is one estimate for a much needed comprehensive system of early childhood care and education (pre-k) in Utah. | |
| Afterschool Programs | $3.6 million | Utah’s 303 afterschool programs serve 43,000 kids but still leave 99,000 unsupervised every day after school. During the 2021 “21st Century Community Learning Center” grant competition in Utah, $1,062,816 was available and there was $4.6 million in requests, indicating a $3.6 million funding gap. | Utah Afterschool Network Director Ben Trentelman |
| Health Insurance: Children: Cover All Kids | $5 million | It would cost Utah about $5 million to remove barriers to health insurance coverage so that all Utah kids can access health insurance. Utah currently ranks last in the nation for covering the one-in-six Utah kids who are Latinx and in the bottom 5 states for all children. Source: Voices for Utah Children and www.100percentkids.health | Voices for Utah Children Ciriac Alvarez Valle |
|
Health Insurance: New parents |
$10 million |
HB 84 would cost $3m to extend post-partum Medicaid coverage for new parents from the current 60 days to one year. HB 85 would cost $7m to extend Medicaid coverage to pregnant women with household incomes up to 200% of poverty level. |
Voices for Utah Children Ciriac Alvarez Valle |
| Mental Health & Substance Use Disorder Treatment | Uncertain |
Utah ranks last in the nation for mental health treatment access, according to a 2019 report from the Gardner Policy Institute. A 2020 report from the Legislative Auditor General found that Utah’s Justice Reinvestment Initiative had failed to achieve its goal to reduce recidivism -- and actually saw recidivism rise -- in part because “both the availability and the quality of the drug addiction and mental health treatment are still inadequate.” (pg 51) Amounts not determined to address large gaps in workforce capacity, but two bills this year are: HB 66: $11m for additional Mobile Crisis Outreach Teams and 2 additional Receiving Centers in rural parts of Utah HB 248: $5m for additional Assertive Community Treatment Teams |
|
| Disability Services | $31 million |
The DSPD disability services waiting list has more than doubled in the last decade from 1,825 people with disabilities in 2011 to 4,427 in 2021. The FY20 $1 million one-time appropriation made it possible to provide services to 143 people from the waiting list, implying that it could cost $31 million to eliminate the waiting list entirely. In the 2022 session, the Legislature added $6 million in ongoing and $3 million in one-time money to shorten the disabilities waiting list. This year, Rep. Ward is sponsoring HB 242 to dedicate additional base budget funding to reduce the waitlist by 200 people each year. |
Legislative Coalition for People with Disabilities – Jan Ferre |
| Rural Utah Economic Development | $20 million | Rural Utahns should not feel that they need to abandon their home communities and add to the growth pressures along the Wasatch Front in order to provide for their families. Rural economic development would benefit all Utahns and reduce disparities between the Wasatch Front and other areas of the state. $20 million was one estimate for funding for economic development projects like the San Rafael Energy Research Center (Emery County) and renewable energy projects around Beaver County, both serving areas where primary jobs such as Smithfield Foods have left recently, and renewable energy projects have the potential to stabilize county economies. | Community Action Partnership of Utah - Stefanie Jones and Clint Cottam – |
| Reduce/Eliminate Benefits Cliffs | Uncertain | The existing benefits cliffs in many public anti-poverty programs – where public assistance disappears suddenly rather than phasing out gradually when someone gets a raise or takes a new, higher-paying job – act as an unintended obstacle to the efforts of low-income people to work their way out of poverty. | Circles Salt Lake – Kelli Parker |
| Sexual and Domestic Violence Victim Services |
$310 million OR $68 million |
Our economy incurs steep economic costs as a result of sexual and domestic violence. The Center for Disease Control estimates that over a lifetime the costs for a female survivor are $103,762 and for a male survivor $23,414. These include medical costs, loss of employment or interruption of paid work, criminal justice system costs, among others. A coalition of victim service providers and state agencies estimates the annual funding needed as $310 million ongoing to meet standard of care for all victims of domestic and sexual violence OR $68 million ongoing to fund the most basic level of services at only the current level of demand for services. |
Erin Jemison, Director of Public Policy, Utah Domestic Violence Coalition (UDVC) |
| Housing | $346 million per year for 10 years |
Among extremely low-income renter households, 71% pay more than 50% of their income for housing, which is considered a severe housing burden. $346 million per year of state funding over the next decade will make it possible to build affordable housing statewide for people earning less than 50% AMI, based on a state cost share of $80,000 per unit, and Utah is short 43,253 units. For more information on the current and ongoing needs visit https://nlihc.org/gap/state/ut |
Utah Housing Coalition Tara Rollins |
| Housing for Seniors | $67.5 million |
$37.5 million a year for 10 years will fund rehabilitation of 500 units per year at a cost of $75,000 per unit. If we don’t fund preservation of affordable housing for seniors we will lose valuable units. $30 million per year will make available rental gap funding of $500 per month for 5,000 units so that seniors can afford to stay in their rented units. https://www.utahhousing.org/preserving-senior-affordable-housing-report.html https://nyuds.maps.arcgis.com/apps/webappviewer/index.html?id=b8318f874017488ea9bdd51a296e59ef for senior housing report |
Utah Housing Coalition Director Tara Rollins |
| Homeless Services | $154 million |
$100m in one-time funds to produce 2,000 units of deeply affordable housing $19m ongoing for tax credits and housing trust fund $5m to the housing trust fund to produce 1,000 new units of affordable housing over the next 10 years $30m one-time for projects to eliminate unsheltered homelessness for families with children: The total number of people needing emergency shelter services in Utah increased by 14% in 2022. For families with children the increase was 33%. This is why, for the first time in over 20 years, families with children were turned away from the family shelter in Midvale during the months of September, October and November of last year because there were not enough beds to meet the need. $30 million would help purchase a motel to convert into a second family shelter and purchase land that can be dedicated to produce mixed income housing developments that include permanent supportive housing for families with children headed by parents with disabling conditions that have been homeless for six or more months. |
|
| Air Quality in Schools | $5 million | Funding to continue the successful implementation of this year’s federally-funded program placing air purifiers in every classroom in Utah, which will reduce the risks both from COVID and from Utah’s air pollution and is expected to result in improved school performance, even more than standard interventions such as reducing class size by 30%, or “high dose” tutoring. (Source: Utah Physicians for a Healthy Environment) | UPHE Director Jonny Vasic - |
| Air Quality: Promote Transit | $25.5 million |
The Utah Transit Authority (UTA) experienced an increase in ridership during Free Fare February in 2022. Tens of thousands of riders, including many new to public transit, enjoyed the services, and stress on our transportation system and environment was lessened. Governor Cox’s Budget Recommendations for FY24 includes a $25 million, one-year pilot for statewide zero-fare transit. This pilot would include the state’s three transit systems that are not currently zero-fare: Cedar Area Transportation System, SunTran, and the Utah Transit Authority. The governor also recommends $500,000 for a zero fare transit study to analyze the impacts of the pilot. During Free Fare February, 87% of entities that subsidize UTA fares for their users continued paying subsidies to help enable the zero fare period. The Governor’s proposal calls on UTA fare subsidy partners to continue paying subsidies for their users during this one-year pilot period to cover $13.1 million in additional costs. This pilot will provide Utah families price relief to help offset the burden of gasoline prices, gasoline tax indexing, and inflation, while also allowing researchers to analyze factors related to permanent decisions about zero fare transit |
|
| Improve UTA transit service | $175.6 million |
$10.9m to match UTA projections to fully supplement free fares for a year. (In all, UTA projected $35.9 in fare revenue for 2023) $3.5 million to address UTA’s driver shortage ($20/hr*2,080 hours*60 operators + 40% for benefits, taxes, etc.) $30,000 to match CATS (Cedar City’s transit system) to fully supplement free fares for a year based on budget projections. $136,000 to match SunTran (St. George’s transit system) to fully supplement free fares for a year based on budget projections. $159 million to clear UTA’s debt to free UTA to expand and improve service. $2 million to fund a matching grant from the federal government to study the feasibility of a passenger rail route connecting Boise to Las Vegas via Salt Lake and points in between. |
Curtis Haring, Utah Transit Riders Union |
| Hunger | $1 million | It is clear that the state needs to do more in providing funding and other resources to help support local community food pantries. | Utahns Against Hunger – Gina Cornia – |
| Utah EITC | $57 million | Last year Utah became the 31st state with our own Earned Income Tax Credit, but we're one of the few who make it non-refundable, even though over 85% of the value of the federal EITC -- and the key to its poverty-reducing and workforce-enhancing power -- is its refundability. In 2022 under Gov. Youngkin, Virginia made their state EITC refundable. ITEP analysis shows 71% goes to the lowest-earning quintile and nearly all to the lower-income half of Utahns. | Voices for Utah Children – Matthew Weinstein – |
| Gov. Cox’s proposed refundable tax credit | $54 million | Utah's Taxpayer Tax Credit shields most low-income workers from the income tax, which is a good thing because it makes our overall tax system less regressive. Now Gov. Cox is proposing to make it even better by making up to $250 of this credit refundable. | Drew Cooper, United Today Stronger Tomorrow |
| Eliminate the sales tax on unprepared food | $200 million | The food tax is the most regressive tax. One-third of it is paid by the lowest-income half of Utah households, who earn less than a sixth of all Utah income. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Economic Research Service, low-income families pay 36% of their income on food while higher-income families spend only 8%. This is why 37 states do not charge any sales tax on food. | Drew Cooper, United Today Stronger Tomorrow |
| Save the Great Salt Lake | $333 million | Gov. Cox is proposing $133m in new resources to save the Great Salt Lake and $200 million to help reduce water waste in agriculture. Source: www.sltrib.com/news/2022/12/30/dear-legislature-heres-2023/ | Utah Rivers Council –Matt Berry |
| Racial Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion as it relates to undocumented Utahns | Our public fiscal policies – how we generate and expend public investment dollars – have a direct impact on whether we are widening or narrowing the gaps between different groups in Utah. The Utah Compact on Racial Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion must be more than just words on a page. slchamber.com/public-policy/utah-compact In particular, Utah is home to 95,000 undocumented men, women, and children. They work hard and pay taxes and need and deserve access to the same public services as every other Utahn. | Comunidades Unidas – Brianna Puga – | |
| The economic case against tax cuts | Tax cuts are usually enacted to provide additional stimulus to the economy. Given our very low unemployment rate, along with ongoing inflationary pressures, now is not really the right time for new economic stimulus. The future is uncertain – some economists expect we may face a recession in the coming year, though there’s a wide variety of opinions about the likely timing and severity of such a possible event. Additional tax cuts right now won’t do much to affect that. However, investing now in the many unmet needs we face, particularly in the areas of water and climate, education, child-care, and the many other needs listed here this morning, will put us in a better position to thrive whatever the coming years bring us in terms of economic conditions. | Univ. of Utah Economics Prof. Thomas Maloney PhD | |
TOTAL |
|
$5.6 billion – over $2b more than the amount of "surplus" revenue for FY2024 |
The press conference was broadcast live on Facebook: https://fb.watch/ieyT_0Zi14/?mibextid=RUbZ1f

Media coverage:
- KJZZ: Local organizations oppose statewide tax cuts, call for investments in Utah's future instead
- Deseret News: Time to invest more in education, housing, water and other areas, group says
- KUTV-2: Local organizers oppose tax cuts, call for investments in Utah's future instead
- KSL: Don't cut taxes, advocacy groups urge Utah lawmakers. Here's why.
- UtahPolicy.com
Additional one-pagers distributed by some of the coalition members:
- Circles Salt Lake: Background about Circles and one-pager about benefits cliffs
- Transit: Utah Transit Riders Union info and one-pager about free-fare transit
- Community Action Partnership of Utah one-pager about rural Utah's needs
- Child care one-pager from UtahCareforKids.org
- Housing affordability one-pager from Utah Housing Coalition
The best holiday gift for Utah kids this year: An improved federal Child Tax Credit
Every December Congress meets to try to pass all the urgent items they didn't manage to get done the rest of the year. Usually the list includes tax policy changes demanded by one well-heeled special interest or another. This year is no different. At the top of the lobbyists' wish list is reportedly "extending soon-to-expire business tax breaks... affecting research and development costs, investment deductions and debt write-offs."
But what about the tax policy issues directly impacting Congress's youngest constituents? It's true that children don't have fancy lawyers and lobbyists and PACs making big campaign contributions. But they do have a few scrappy nonprofits speaking up for their interests and backed by millions of parents. And at the top of the children's wish list this month is improvements to the federal Child Tax Credit.
The federal CTC does a world of good every year for families all over Utah and across the nation. Well over a third of Utahns qualify for the CTC every year when they file their taxes. That's over half a million households! And the amount of the CTC received by these Utah families exceeds $1.6 billion -- that's billion with a b. Wow!
But there is a problem with the Child Tax Credit. Tens of thousands of Utah families fail to qualify every year for the full credit of $2,000 per child for a simple reason: The parents work low-wage jobs -- often working long hours -- but their low hourly wages still leave their incomes below the minimum level required under current tax law to qualify for the full credit -- over $29,000 of income for a single parent with two kids, for example. In other words, a single mom working full-time at $12/hour makes too little to qualify for the full CTC under its current rules.
That means over 150,000 Utah kids every year are left out and left behind -- and these are the very kids who would benefit most from the proven positive impacts of refundable tax credits like the CTC -- including better educational outcomes and higher labor force participation rates years later when they become adults.
And it gets worse: While most of the kids excluded from the CTC are white, disproportionate numbers of them are from Utah's communities of color, including an estimated 50,000 Latino children, comprising 29% of Utah’s Latino child population, as well as 6,000 Native American children, comprising 75% of Utah’s Native American children. This means that a tax credit that has incredible potential to reduce societal disparities is instead making them worse.
That's a real shame, because the CTC does a lot to reduce child poverty already. National data from the Census Bureau's Supplemental Poverty Measure has found that refundable tax credits, including both the Child Tax Credit and Earned Income Tax Credit, reduced child poverty from where it would have been -- 18% or one-in-six children -- to 12.5% or one-in-eight children in 2019. That's over 4 million children lifted out of poverty. And if we could make the full CTC available to all the lower-income kids now being left out, that would help an additional 19 million children who need the help most.
Even if Congress lacks the political consensus to restore the temporary 2021 CTC boost that cut child poverty last year by 36%, there are several more incremental ideas that would help a lot of kids:
- Implement a more rapid phase-in of the refundable credit, as proposed by Sen. Mitt Romney in his Family Security Act 2.0 proposal from earlier this year.
- Make the full credit available without a phase-in for families with children under the age of 6.
- Exempt from the phase-in grandparents acting as custodial parents and parents whose disabilities impact their ability to work.
- Institute a look-back policy that counts previous years' earned income in determining whether a work requirement has been met.
- Restore the pre-2017 status quo where all children in immigrant families could receive the CTC.
The role of Utah's Congressional delegation in any Child Tax Credit improvements passed this month is expected to be one of the keys to success. After all, it was Utah Senator Mike Lee who demanded that Congress include improvements to the CTC in the 2017 TCJA legislation (though that law also cut off an estimated 1 million immigrant children without Social Security numbers from the credit). And it is Senator Romney who has put far-reaching additional improvements on the table with his Family Security Act proposals.
If you agree that Congress should act this month to improve the Child Tax Credit, let your Representative and our two Senators hear from you! Lifting more kids out of poverty would truly be a wonderful holiday gift for Utah's children this year.